The debate between steel structures and reinforced cement concrete (RCC) is a critical one in construction. Both materials have unique properties, making them suitable for different applications. Deciding which to use depends on factors such as budget, project type, environmental considerations, and long-term performance requirements.
In this article, we compare steel structures and RCC to help you make an informed choice for your construction projects.
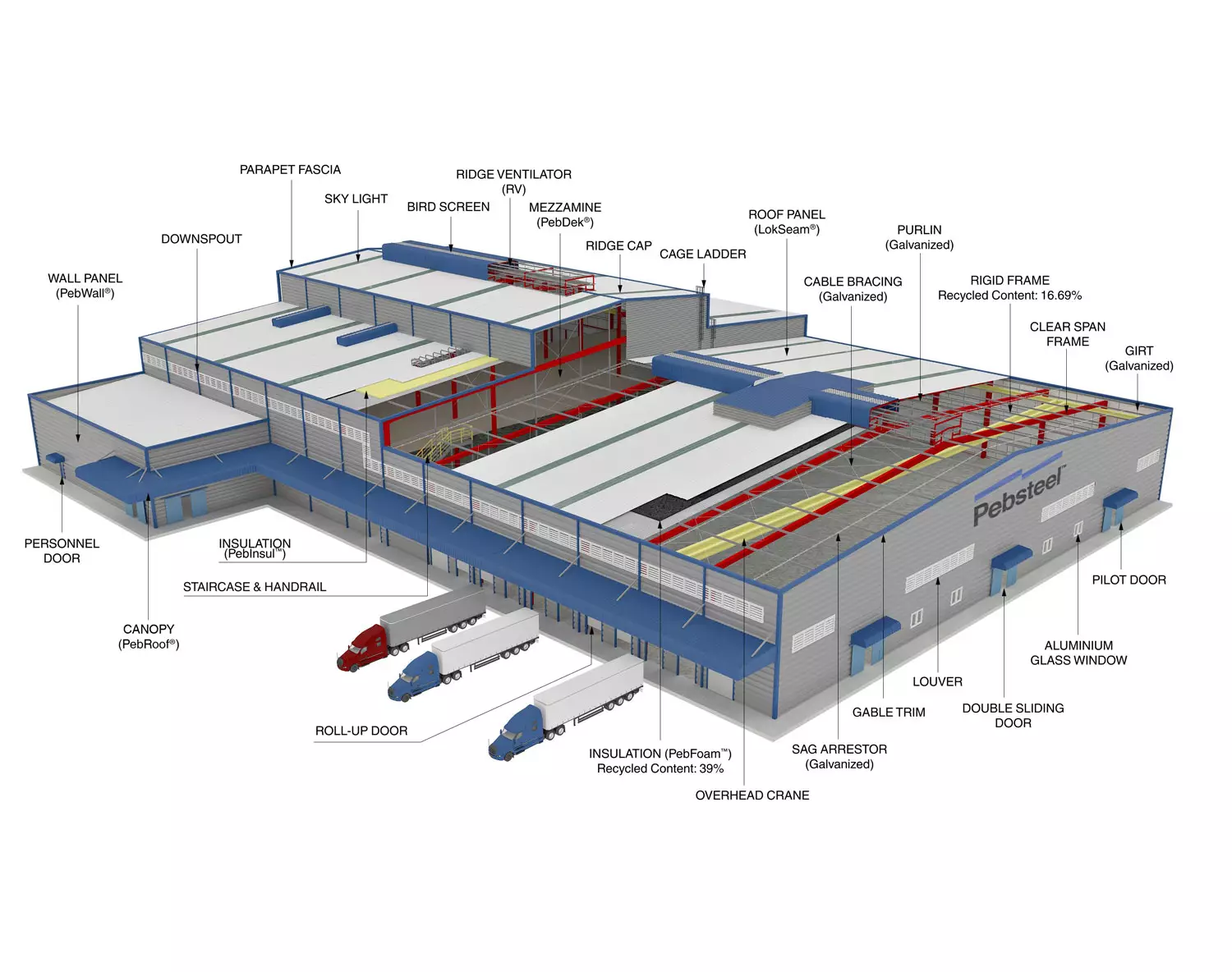
What is a Steel Structure?
Steel structure is a versatile and durable material that is used in a wide variety of applications. It is strong, lightweight, and relatively easy to work with, making it a popular choice for many different types of construction projects.

Key Features:
• High strength-to-weight ratio
• Prefabrication-friendly
• Resistant to pests and environmental damage
What is RCC (Reinforced Cement Concrete)?
RCC is a composite material made by embedding steel reinforcement bars (rebars) within concrete to improve its tensile strength. RCC is widely used in infrastructure projects such as bridges, dams, and multi-storey buildings.

Key Features:
• High compressive strength
• Long-lasting durability
• Suitable for heavy loads
Steel Structure vs RCC: A Head-to-Head Comparison
1. Strength and Durability
• Steel Structure: Offers superior tensile strength, making it ideal for high-rise buildings and structures subjected to dynamic forces like wind or earthquakes.
• RCC: Excels in compressive strength and is better suited for applications with heavy static loads, such as dams or foundations.
2. Construction Speed
• Steel Structure: Prefabrication allows for quick assembly, reducing construction time significantly.
• RCC: Requires onsite pouring, setting, and curing, which can extend the project timeline.
3. Cost Efficiency
• Steel Structure: Higher upfront material costs but lower labour costs and faster construction reduce overall expenses.
• RCC: Lower material costs but higher labour and extended timelines can offset savings.
4. Flexibility and Adaptability
• Steel Structure: Highly flexible, allowing for custom designs and modifications even after construction.
• RCC: Less adaptable; alterations can be complex and costly.
5. Environmental Impact
• Steel Structure: Recyclable and less wasteful, making it an eco-friendly option.
• RCC: Produces significant carbon emissions during cement production and generates more waste.
6. Load Handling
• Steel Structure: Ideal for light to moderate loads with flexibility for dynamic forces.
• RCC: Best for heavy static loads, like foundations and dams.
7. Aesthetic Versatility
• Steel Structure: Allows for sleek, modern designs and integration with other materials like glass.
• RCC: Typically results in bulkier designs and is less visually appealing without extensive finishing.
8. Maintenance
• Steel Structure: Requires regular inspection and anti-corrosion treatments.
• RCC: Lower maintenance requirements but may develop cracks over time.
Applications of Steel Structures

• High-Rise Buildings: Due to their strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to dynamic forces.
• Industrial Facilities: Suitable for warehouses, factories, and workshops.
• Bridges: Preferred for long spans and flexibility.
• Temporary Structures: Quick assembly and disassembly make steel ideal for relocatable buildings.
Applications of RCC
• Dams and Reservoirs: Superior for handling heavy loads and water pressure.
• Foundations: Provides a stable base for structures with significant weight.
• Infrastructure: Commonly used in roads, bridges, and tunnels.
• Multi-Storey Buildings: Often used for low to mid-rise constructions.
Steel Structure vs RCC: Cost Analysis
Initial Costs
• Steel Structure: Higher material costs due to the quality and precision of prefabrication.
• RCC: Lower material costs but more labour-intensive.
Lifecycle Costs
• Steel Structure: Lower maintenance and faster construction offset higher upfront costs.
• RCC: Extended maintenance and repair can increase long-term expenses.
Advantages of Steel Structures
1. Speed of Construction: Prefabricated components ensure rapid assembly.
2. Flexibility: Suitable for modifications and expansions.
3. Sustainability: Fully recyclable and generates less waste.
4. Aesthetic Appeal: Supports innovative and modern designs.
Advantages of RCC
1. Strength: High compressive strength makes it ideal for load-bearing applications.
2. Availability: Materials like cement and sand are readily accessible.
3. Versatility: Used in a wide range of infrastructure projects.
4. Fire Resistance: RCC is highly fire-resistant compared to steel.
Challenges with Steel Structures
1. Corrosion: Requires protective coatings in humid or corrosive environments.
2. Initial Cost: Higher upfront costs compared to RCC.
3. Skilled Labour: Needs specialised labour for fabrication and assembly.
Challenges with RCC
1. Cracking: Prone to shrinkage and cracks over time.
2. Environmental Concerns: Cement production generates significant CO₂ emissions.
3. Long Construction Time: Requires curing and setting before completion.
Choosing Between Steel and RCC

When to Choose Steel Structures
• For projects requiring speed and flexibility.
• When modern aesthetics or lightweight designs are a priority.
• In areas with high seismic activity or strong winds.
When to Choose RCC
• For projects demanding high compressive strength, like dams and bridges.
• When budget constraints favour lower material costs.
• For permanent infrastructure projects with heavy static loads.
Both steel structures and RCC have their strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different applications. Steel structures are ideal for modern, flexible, and eco-friendly designs, while RCC remains the go-to choice for heavy, static, and cost-sensitive projects.
By understanding the specific needs of your construction project, you can make an informed decision that balances performance, cost, and sustainability. Whether you choose steel or RCC, the right material will ensure the success and longevity of your structure.












Comments